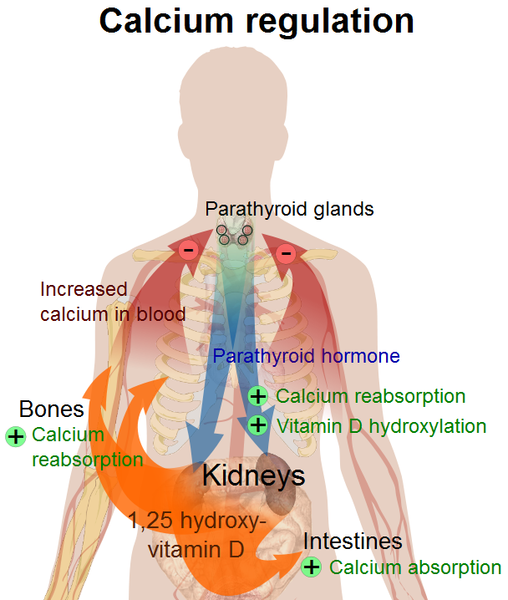
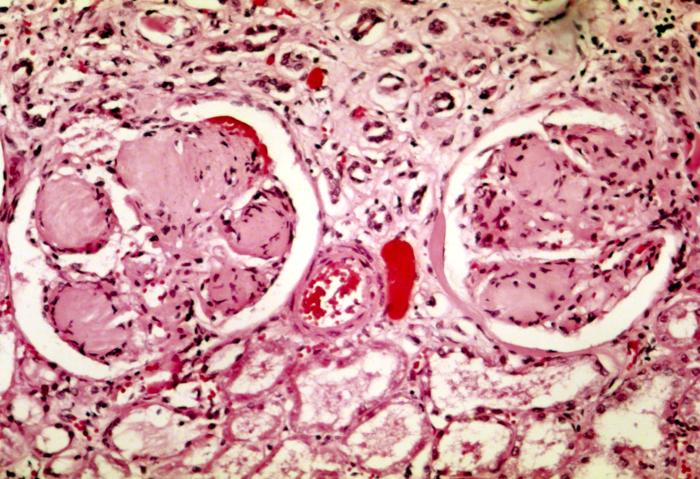
Causes of Hypocalcemia 1. Artifact (low serum albumin; rapid volume expansion) 2. Hypoparathyroidism 3. Pseudohypoparathyroidism 4. Postoperative resection of parathyroid … Read More »
Introduction to Body Calcium and Vitamin D
Calcium Calcium is a major constituent of bone and hence an important structural element in the body. Plasma Calcium The … Read More »
Hypoglycemia and its Causes
A working definition of clinical hypoglycaemia is a low blood glucose level less than 3.0 mmol/l, associated with characteristic, but … Read More »
Differences between Hyperosmolar Non-Ketotic Hyperglycaemic Coma and Diabetic Ketoacidosis
The differences between diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic non-ketotic hyperosmolar coma are: Diabetic ketoacidosis Non-ketotic hyperosmolar coma Definition Triad of: hyperglycemia, … Read More »
Diagnostic Criteria and Complications of Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes is diagnosed if: a. HbA1C ≥ 6.5%, OR b. Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) ≥ 126 mg/dl (7.0 mmol/l), OR c. … Read More »
Classification of Diabetes Mellitus
WHO Definition of Diabetes Mellitus A state of chronic hyperglycaemia which may result from genetic or environmental factors often acting … Read More »
Causes of Hyperglycemia
Fasting blood glucose level higher than 126 mg/dl or 7.0 mmol/l is labeled as hyperglycemia. Fasting hyperglycaemia may occur in … Read More »
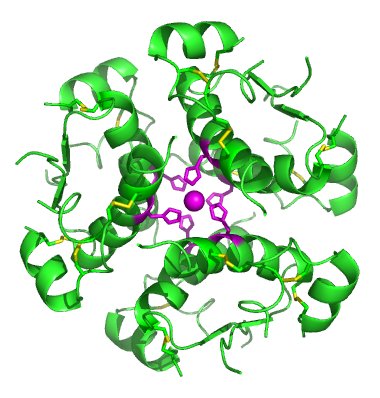
Structure of Insulin
Insulin is a hormone secreted by beta cells within the pancreas. It is essential in regulating the metabolism of carbohydrates and … Read More »
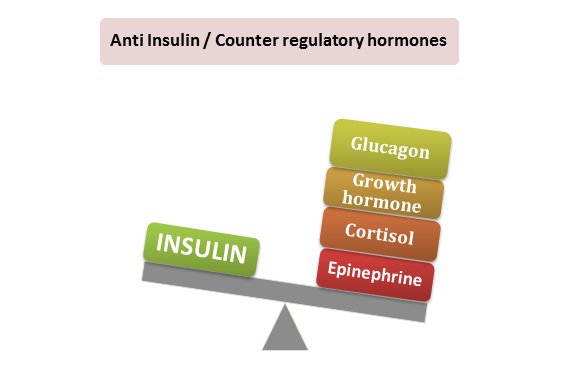
Hormones Regulating Carbohydrate Metabolism
Several hormones regulate carbohydrate metabolism. Insulin It is secreted by the beta-cells of the pancreas in response to a high … Read More »
Piperazine Citrate and Diethylcarbamazine -Antihelminthic Drugs
The article is a continuation of basics of antihelminthics. General Adverse Drugs Reactions of Antihelminthics 1. Intestinal Actions Intestinal actions … Read More »
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself