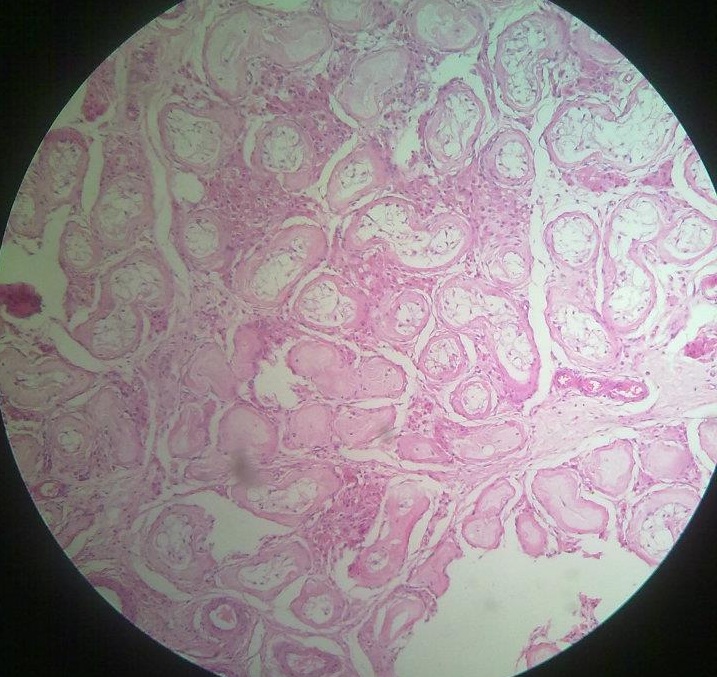
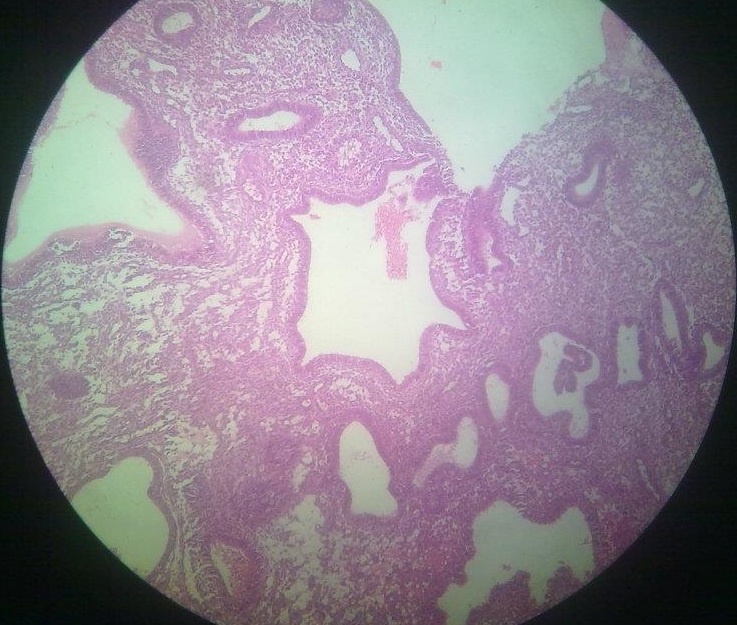
Pigments Pigments are defined as substances occurring in living matter that absorb visible light. Classification Pigments are classified as: Endogenous … Read More »
Metaplasia
Metaplasia is a reversible change in which one differentiated cell type (epithelial or mesenchymal) is replaced by another cell type. … Read More »
Atrophy
Atrophy may be defined as the shrinkage in size of cell by loss of cell substance, resulting in decreased functional … Read More »
Hyperplasia
Hyperplasia constitutes an increase in number of cells in an organ or tissue which may then have increased volume. It … Read More »
Caseous Necrosis
Necrosis It is a spectrum of morphological changes that follow cell death in living tissues, resulting from progressive degradative action … Read More »
Coagulative Necrosis
Coagulative necrosis is the most common pattern of necrosis characterized by denaturation of cytoplasmic proteins, cellular swelling and breakdown of … Read More »
Fatty Change
Fatty change is the abnormal accumulation of triglycerides within parenchymal cells. It is most commonly seen in liver, which is … Read More »
Hydropic Change
Hydropic change or cellular swelling or vacuolar degeneration is one of the factors of reversible cell injury, which can be … Read More »
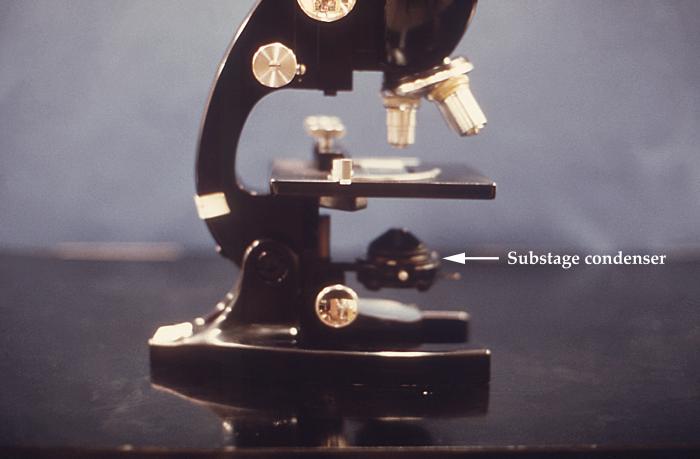
Study of a Compound Microscope
Principle The working principle of microscope is to show large image of those objects which cannot be seen with the … Read More »
Acetazolamide, Sulthiame and Newer Antiepileptics
Acetazolamide Not commonly used for treatment of epilepsy. Only effect is due to acidosis produced, being more effective in petit … Read More »
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself