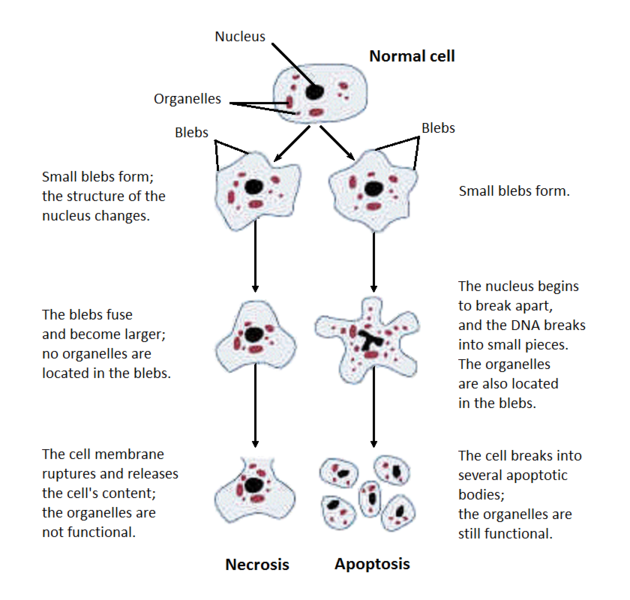
Atrophy may be defined as the shrinkage in size of cell by loss of cell substance, resulting in decreased functional … Read More »
Hyperplasia
Hyperplasia constitutes an increase in number of cells in an organ or tissue which may then have increased volume. It … Read More »
Caseous Necrosis
Necrosis It is a spectrum of morphological changes that follow cell death in living tissues, resulting from progressive degradative action … Read More »
Coagulative Necrosis
Coagulative necrosis is the most common pattern of necrosis characterized by denaturation of cytoplasmic proteins, cellular swelling and breakdown of … Read More »
Fatty Change
Fatty change is the abnormal accumulation of triglycerides within parenchymal cells. It is most commonly seen in liver, which is … Read More »
Hydropic Change
Hydropic change or cellular swelling or vacuolar degeneration is one of the factors of reversible cell injury, which can be … Read More »
Differences Between Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis
S/N Crohn’s Disease Ulcerative Colitis 1 Involvement of Wall Transmural Confined to mucosa and submucosa 2 Thickness of Wall Thick … Read More »
Laboratory Diagnosis of Cancer
Tumor Diagnosis 1. Imaging: X-ray Ultrasound CT scan MRI 2. Tumor markers (may be specific for specific tumors) Receptors Hormones … Read More »
Invasion and Metastasis -Mechanism and Pathway
Epithelial and mesenchymal cancer cells have to invade: Basement membrane Capsule (if present) Penetrate surrounding stroma resulting in local invasion … Read More »
Characteristics of Benign and Malignant Tumors
Differentiation Definition The extent to which tumor cells resemble the cell of origin. Resemblance to parent cells or cells of … Read More »
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself