Insulin is a hormone secreted by beta cells within the pancreas. It is essential in regulating the metabolism of carbohydrates and … Read More »
Hormones Regulating Carbohydrate Metabolism
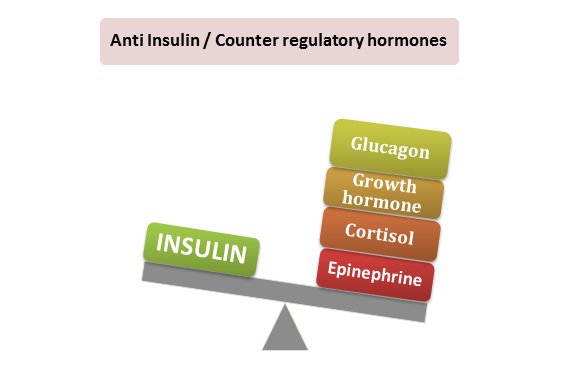
Several hormones regulate carbohydrate metabolism. Insulin It is secreted by the beta-cells of the pancreas in response to a high … Read More »
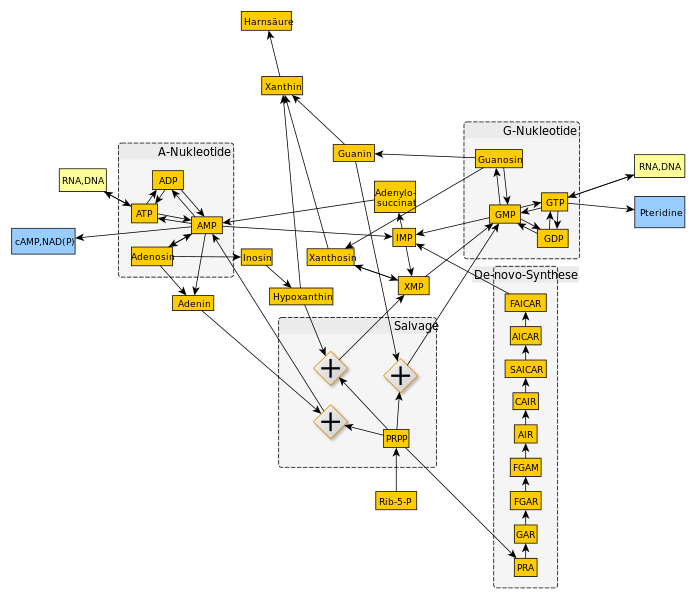
Purine Metabolism
The purine base (adenine, guanine, hypoxanthine, etc.) is a double ring structure. A base attached to pentose (ribose) is a … Read More »
Causes of Hyperuricemia and Hypouricemia
Hyperuricemia The causes of hyperuricemia may be primary or secondary. Primary Overproduction: Idiopathic Lesch-Nyhan syndrome Glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency Reduced excretion: Idiopathic … Read More »
Inborn Errors of Purine Metabolism
Inborn errors of purine metabolism include the following: 1. Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase Severe deficiency (Lesch-Nyhan syndrome) The Lesch-Nyhan syndrome is … Read More »
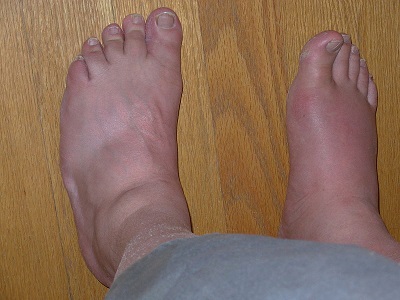
Gout -Stages, Diagnosis and Investigations
Gout is a group of metabolic diseases associated with hyperuricaemia and deposition of crystals of monosodium urate in tissues. Presentation … Read More »
Differential Diagnosis of Joint Pain
Differential diagnosis of joint pain includes the following: Traumatic Causes Bones Patellar fractures Supracondylar fractures of femur Tibial fractures involving … Read More »
Monitoring Reperfusion after Thrombolytic Therapy
Early monitoring of markers may be useful to determine reperfusion success in patients receiving thrombolytic therapy. The complete opening of … Read More »
Investigations of Acute Coronary Syndrome
Laboratory investigations (Other than cardiac markers) Plasma glucose- fasting and after break fast (ABF) HBA1c (glycosylated haemoglobin) Microalbuminaemia (spot urine … Read More »
Cardiac Markers and their Pattern of Release
A cardiac marker is a clinical laboratory test that is useful in the detection of acute myocardial infarction or minor … Read More »
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself