Predisposing Factors of Infant Mortality
Biological Factors
• Birth weight, Age of the mother, Birth order, Birth spacing, multiple births, Family size, high Fertility.
Economic Factors
• Low socioeconomic factors, quality & availability of health care
Cultural & Social Factors
• Breast feeding, Early marriage, maternal education, etc
Infant Mortality Causes
Neonatal Mortality (0-4wks) Causes
1. Low Birth weight
2. Prematurity
3. Birth injury/difficult labour
4. Sepsis
5. Congenital anomalies
6. Hemolytic disease
7. Placenta/cord conditions
8. Diarrheal disease
9. Acute resp. diseases
Post-neonatal Mortality (1-12 months)
1. Diarrheal disease
2. Acute respiratory diseases
3. Communicable disease
4. Malnutrition
5. Congenital anomalies
6. Accidents
Management & Prevention of Infant Mortality
1. Prevention of Unwanted Pregnancies
2. Identification of High Risk
3. Management of High Risk
1. Prevention of Unwanted Pregnancy
Prevention of unwanted pregnancy through:
• Health Education
• Family Planning
• Genetic Counseling
2. Identification of High Risk
a. High Risk Pregnancy
• Extremes of age
• Grandmultiparae
• Intrauterine infections
• Bad obs. History
• Pre-existing Illness
b. High Risk New Born
• Prematurity
• Low Birth weight
• Congenital Anomalies
• Sepsis
• Babies born to mother with chronic disease
3. Management of High Risk
• Early detection of High Risk Pregnancy
• Antenatal care
• Natal care
• Postnatal Care
• Identification of High risk babies
Management of High Risk New Born
• Nursery Intensive care
• Medical Surveillance
• Nutritional Surveillance
• Social Monitoring after discharge from the nursery
• Follow up in the under 5 clinic
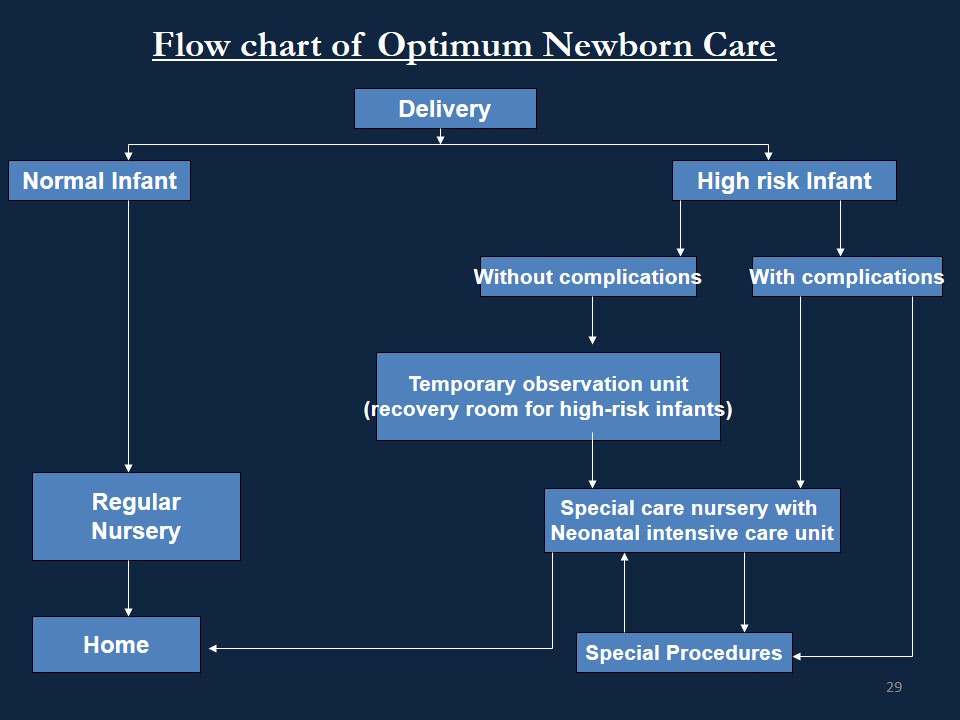
Care of the Baby
a. Immediate Care
b. Late Neonatal Care
Immediate Care
• Clearing the airway
• APGAR score
• Care of the cord
• Care of the eyes
• Care of the skin
• Maintenance of body temperature
• Breast feeding
Late Neonatal Care
• Immunization
• Growth Monitoring
• Nutritional Surveillance
Prevention of Child Morbidity and Mortality
• Prenatal Nutrition
• Prevention of infections especially tetanus
• Immunization
• Breast feeding
• Growth monitoring
• Family planning
• Sanitation
• Provision of primary health care
• Socio-economic development
• Family planning
• Health Education
• Screening for occult treatable condition
• Prevention of Specific Health Problems
Screening for occult treatable conditions
In preventable diseases especially those with clear symptoms, screening would be helpful :
• Anemia
• Congenital hypothyroid
• Visual Impairment
• Physical growth & development
• BP management in 3 yrs and above
• Hearing Impairment
Prevention of Specific Health Problems
a. Injuries/ Accidents
b. Psychological Problems
c. Dental Problems
a. Injuries/ accidents
• Modification of hazards.
• Use of the products with child proof caps.
• Lowering of temperature of hot H2O heaters.
• Installation of window guards.
• Modification of behavior
• Motor cycle helmets
• Infant car seats.
b. Psychosocial problems
Psychological problems will develop due to the environment, birth conditions and developmental delays. These can be prevented if children are properly screened.
Give preventive and remedial educational and psycho therapeutic services.
c. Dental problems
Which are of great concern in child morbidity & they can be prevented by:
• Regular Oral Hygiene
• Reduction of sugar in food, drinks and medicine.
• Community water Fluoridation
• Topical fluoride application
Minimum Number of Visits made to assess the Child Health Problems
Visits in the 1st year of life:
Once every month,12 visits
Visits in 1 – 5 years of life:
Once in 3 months, 4 visits in a year
Priority Areas to Improve Newborn Health
a) Before & during Pregnancy
b) During Pregnancy
c) During & soon after Delivery
d) During the First Month of Life
a. Before & during Pregnancy
• Well-timed, well-spaced, & wanted pregnancies
• Well-nourished & healthy Mother
• Pregnancy free of drug abuse, tobacco & alcohol
• Tetanus & rubella immunization
• Prevention of mother to child transmission of HIV
• Female education
b. During Pregnancy
• Early contact with health system
• Birth & emergency preparedness
• Early detection & treatment of maternal complications
• Monitoring of fetal well-being & timely interventions for fetal complications
• Tetanus immunizations
• Prevention & treatment of infections (malaria, hookworm etc)
• Good diet
• Prevention of violence against women
c. During & Soon After Delivery
• Safe & clean delivery by skilled attendant
• Early detection & prompt management of delivery and fetal complications
• Emergency obstetric care for maternal and fetal conditions
• Newborn resuscitation
• Newborn care ensuring warmth & cleanliness
• Newborn cord, eye & skin care
• Early initiation of exclusive breast feeding
• Early detection & treatment of newborn complications
• Prevention & control of infections
• Information & counseling on home care, danger signs & care seeking
d. During the First Month of Life
• Early post-natal contact
• Protection, Promotion & support of exclusive breast feeding
• Prompt detection & management of disease in newborn infant
• Immunization
• Protection of girl child
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself