The force exerted by blood against vessel wall
► Arterial blood pressure fluctuates in relation to ventricular systole and diastole
► Normal arterial blood pressure
120/80 mm Hg (100-140/60-90 mm Hg)
Mean Arterial Blood Pressure (MAP)
► Average pressure in arteries through out cardiac cycle
► Mean driving force propelling the blood through microvessels
► MAP = DBP + 1/3 of pulse pressure
MAP = 80 + 13 = 93 mm Hg
Why necessary??
► To ensure sufficient driving force
► To avoid extra work load on heart
► To avoid vascular damage
Determinants of blood pressure
MAP = CO x TPR
-
- CO (cardiac out put)
• SV x HR
-
- TPR (total peripheral resistance)
• Sympathetic nervous system activity
• Distensibility of the vessels
-
- Blood Volume
By controlling CO, TPR and blood volume blood pressure is regulated
► Short term regulation
► Rapid regulation of MAP – within seconds
► Neurally mediated – autonomic reflexes
► Acts by altering CO and TPR
► Long term regulation
► Slow regulation of MAP – within minutes, hours, days or months
► Hormonally mediated
► Through regulation of blood volume by kidneys
Short term regulation of BP
► Regulates minute to minute variations in BP
► Responds within seconds
► Accomplished by
► Alterations in CO and TPR by
► Autonomic sympathetic reflexes
► Organs affected are
► Heart
► Arteries
► Veins
► Autonomic sympathetic reflexes
► Baroreceptor reflex
► Chemoreceptor reflex
► CNS ischaemic response
Baroreceptor reflex
► Baroreceptors (high pressure receptors)
► Carotid sinus baroreceptors
► Aortic arch baroreceptors
► Control BP by -ve feed back manner
► Responds more to rapidly changing pressure
► Inhibitory to vasomotor center
► BP buffering function
► Buffers minute to minute variations in BP related to body posture
► Resetting of baroreceptors
► Inability of baroreceptors to regulate persistent change in BP
► Disorders of baroreceptor reflex
► Orthostatic hypotension
► Vasovagal syncope
► Various stimuli (emotional disturbance)
► Inhibition of sympathetic system
► Stimulation of parasympathetic system
► Carotid sinus message
► Supraventricular tachycardia
► Carotid sinus syncope
► Tight collar syndrome
Cardiovascular Center
► located bilaterally in medulla and lower pons
§ Vasomotor center (sympathetic system)
• Vasoconstrictor area (rostral ventrolateral medulla)
q Sympathetic stimulation
• Vasodilator area (caudal ventrolateral medulla)
q Sympathetic inhibition (inhibitory to RVLM)
§ Cardiostimulatory center (sympathetic & vagal)
§ Cardioinhibitory center (sympathetic & vagal)
§ Sensory area – nucleus of tractus solitarius (terminus of IX & X cranial nerves)
► Inputs
§ From higher centers
• Cerebral cortex, limbic system, hypothalamus
§ From periphery
• Baroreceptors
• Chemoreceptors
► Outputs
§ To heart, arteries and veins through autonomic nervous system
Chemoreceptor reflex
► Chemoreceptors
► In carotid and aortic bodies
► Sensitive to ¯ PO2, CO2, H+ (¯ pH)
► Stimulate at BP < 80 mm Hg
► Stimulatory to vasomotor center
► Share the pathway with baroreceptor reflex
CNS ischaemic response
► Intense response of vasomotor center to cerebral ischaemia
► Stimulation of vasomotor center at BP < 60 mm Hg (especially < 15 – 20 mm Hg)
► Last ditch stand – an attempt to rise BP
Cushing reaction
► When CSF pressure ≥ arterial pressure
► Blood supply to brain depressed
► Stimulation of vasomotor center
► Protects vital centers in brain if CSF pressure rises high enough
Low pressure receptors
► Present in both atria, pulmonary arteries, pulmonary veins and vena cavae – cardiopulmonary receptors
► Detect change in blood volume
► Share the pathway with aortic baroreceptors
► Affect vasomotor center accordingly
Bainbridge reflex
► heart rate due to rise in atrial pressure
► Low pressure receptors in atria ® vagus ®
► Vasomotor center ® sympathetic & ¯ vagal activity ® increased heart rate
► Prevents damming of blood
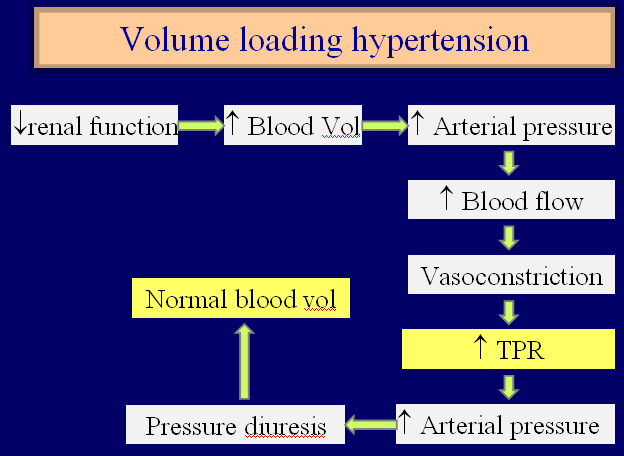
Long term regulation of arterial pressure
► Blood Volume is the determinant to be regulated to control BP on long term basis
Water intake = Water output
► Salt (osmolarity) affects body water
Salt & water intake = Salt & water output
► Renal function curve
► More the mean arterial pressure more will be the urinary volume output
► Pressure diuresis
► Increased urine volume output due to rise in arterial pressure
► Pressure natriuresis
► Increased Na+ output due to rise in arterial pressure
► Water and salt output must equal intake over a long period
► Infinite gain of renal BP regulating mechanism
► Correction/error (0)
► Two basic factors affecting long term regulation of BP
► Renal function curve
► Water and salt line
► Arterial pressure determines the balance between salt and water intake and output
Renin angiotensin system
► Augments renal function by enhancing water & salt reabsorption on long term basis
► Causes vasoconstriction
► Renin
► Secreted from juxtaglomerular cells in response to ¯ arterial pressure
► Angiotensin II (indirect actions)
► Causes release of aldosterone from adrenal glands
► Causes release of ADH from hypothalamus
► Stimulates thirst mechanism
► Aldosterone
► Causes reabsorption of salt and water
Other slow adjustments
► Capillary fluid shift
► BP ®Pc ® fluid shift out of capillary
► Stress relaxation
► stretch on vessel wall ® relaxation of vascular smooth muscle
Hypertension
► Persistently elevated mean arterial pressure of more than 110 mm Hg (>140/90 mm Hg)
► Secondary hypertension
► Secondary to some primary problem
► Renal, cardiovascular, endocrine , neurogenic etc
► Primary (essential/idiopathic) hypertension
► Cause not known
Coarctation of aorta
► Blockage in aorta distal to arterial branches to head and arms but proximal to renal arteries
► Arterial pressure in
► lower body is normal
► Upper body high

 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself