Corticosteroids are used in several diseases of the eyes, the important ones are given below, followed by the contraindications of using corticosteroids:
- Chalazion
- Atopic Dermatitis
- Chronic blepheritis
- Childhood blepharokeratoconjuctivitis
- Graves Ophthalmolopathy (?)
- Proptosis
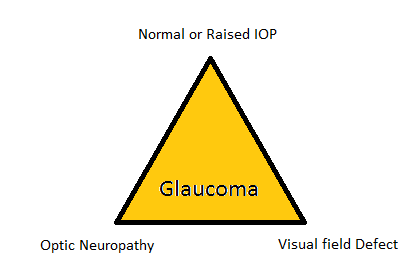
- Optic neuropathy
- Idiopathic orbital inflammatory disease
- Orbital myositis
- Tolosa Hunt syndrome
- Wegner’s granulomatosis
- Capillary hemangioma
- Sjogren’s syndrome
- Acute bacterial conjunctivitis (for scarring and membranes)
- Adenoviral conjuctivits (for membranes and pseudomembranes)
- Allergic conjunctivitis
- Mechanically induced papillary conjunctivitis
- Mucous membrane pemphigoid
- Stevens-Johnson’s syndrome
- Superior limbic keratoconjuctivitis
- Lignous conjunctivitis
- Pingueculum
- Pterygium
- Conjuctivochalazia
- Bacterial keratitis (to prevent scarring, chance for fungi, herpes simplex and mycobacterial growth and delayed epithelial healing)
- Disciform keratitis (compulsory)
- Necrotizing stromal keratitis
- Acute shingles
- Syphilitic interstial keratitis
- Cogan syndrome
- Protozoal keratitis
- Onchocerciasis
- Marginal keratitis
- Phylctenulosis
- Ocular rosacea
- Mooren ulcer
- Terrien marginal degeneration
- Thygeson superficial punctuate keratitis
- Infective scleritis
- Cystoid macular edema
- Simple episcleritis
- Nodular episcleritis
- Acute congestive angle closure glaucoma
- Rubeosis iridis
- Uveatic glaucoma
- Posner-Schossman syndrome
- Traumatic glaucoma
- Uveitis
- Toxocariasis
- Cysticercasis
- Herpes simplex uveitis (only in absence of epithelial disease)
- Acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (?)
- Multifocal choroiditis and panuveitis
- Serpiginous choroidopathy
- Progressive subretinal fibrosis and uveitis syndrome
- Vogt-Keyanagi Harada syndrome
- Sympathetic Ophthalmitis
- Birdshot retinochoroidopathy
- Fuch’s uveitis syndromes
- Phacoanaphylactic endophthalmitis
- Phacogenic non-granulomatous uveitis
- Solitary idiopathic choroditis
- Frosted branch angitis
- Pyogenic granuloma
- Eale’s disease
- Radiation retinopathy
- Demyelinating optic neuritis
- Sarcoid optic neuritis
- Neuroretinitis
- Giant cell arteritis
- Diabetic papillopathy
- Orbital fractures (for edema)
Contraindications:
- Tuberculosis
- Viral infections (relative)
- Bacterial infections (relative)
- Fungal infections (almost absolute)
- Peptic ulcer
- Deep corneal epithelial defects
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself