Taste – chemical sense
§Taste receptors are
§Chemical receptors
§Located in taste buds
§Linked with primitive emotional and behavioral functions of CNS (licking & disliking of food)
Important in selection & enjoyment of food
§Strongly linked with sense of smell § Also influenced by
►Vision, temperature, pain & touch sensations
►Metabolic needs of body & past experiences with the food
§Flavors are generally combinations of taste & smell
PRIMARY SENSATIONS OF TASTE
§4 established basic tastes
►Salty
§Ionized salts mainly Na+
►Sour
§Acids (H+) more acidic food → more sour taste
►Sweet
§Mainly organic substances e.g. sugars, alcohols, glycols, aldehydes etc.
►Bitter
§Long chain organic substances having nitrogen
§Alkaloids (quinine, nicotine, caffeine etc.)
5th additional taste
§ Umami (meaty taste)
§ Glutamate and monosodium glutamate
§All other tastes are combinations of the 5 basic tastes
LOCATION OF TASTE BUDS
§Taste receptors are present in taste buds
§Taste buds are present in
§Gustatory papillae of tongue (mainly)
§Hard/soft palate
§Epiglottis
§Pharynx
§Proximal esophagus
§Tonsillar pillars
GUSTATORY PAPILLAE OF TONGUE
Small projections on upper surface of tongue
Give rough appearance to the tongue Contain taste buds
4 types
Circumvallate papillae (wall like)
§‘V’ shaped row of 7-10 papillae on posterior part of tongue
§100-300 taste buds per papilla (most numerous)
§Innervated by IX nerve
Fungiform papillae (mushroom like)
§Anterior 2/3rd of tongue
§Up to 5 taste buds per papilla §Innervated by VII nerve
Foliate papillae (leaf like)
§Lateral borders of tongue
§Moderate number of taste buds
§Most of the taste buds degenerate in childhood
§Innervated by VII and IX nerves §Filiform papillae (thread like) §Scattered on entire dorsal surface of tongue
§No taste buds
§Have tactile receptors
§Increase friction between food particles & tongue
TASTE BUDS
§Sense organs for taste
§3000-10,000 taste buds in adults (more in children)
§Diameter 1/30 mm and length 1/16 mm §Degenerate after 45 yrs
§Contain about 50 modified epithelial cells
§Each taste bud – specific for one primary sensation in low conc.
Cell types
§Basal cells
§Sustentacular cells
§Gustatory receptor cells
§Outer tips arranged around taste pore §Contain microvilli or taste hairs
§Microvilli contain receptors & are exposed to testants
§Make synaptic connections with sensory nerve fibers
§Life span about 10 days
§Basal cells form new receptor cells Gustatory receptor cell
Taste buds mediating a primary sensation of taste are located in particular areas on tongue
Sweet & Salty tastes – tip of tongue
Sour taste – two lateral sides of tongue
Bitter taste – posterior tongue & soft palate
Overlap b/w all the areas
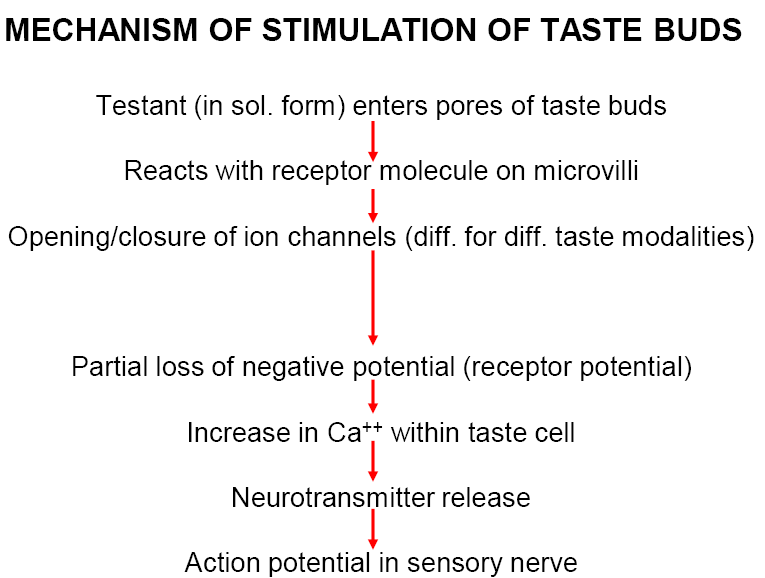
MECHANISM OF STIMULATION OF TASTE BUDS
§Salty taste
§Salts (Na+) depolarize salt receptor cells by opening epithelial Na channel (ENaC)
§Sour taste
§Acids depolarize sour receptor cells by
§Activating H+ – gated cation channels §Inactivating K+ channels
Sweet taste (2nd messenger system)
§G protein → activation of adenylyl cyclase → increased cAMP → decreased K+ conductance
§Bitter taste (2nd messenger system)
§Increased inositol triphosphate (IP3) production → increased intracellular Ca2+ → release of synaptic transmitter
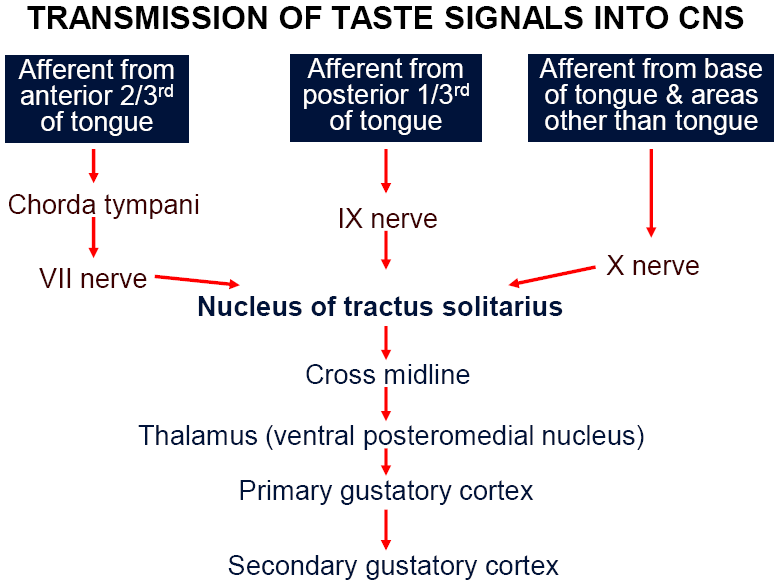
OTHER CONNECTIONS
§Taste reflexes
§Signals to inferior and superior salivatory nuclei from nucleus of tractus solitarius
§Control secretions saliva
§Fibers also go to hypothalamus and limibic system
§Linkage of taste sense to emotions
ADAPTATION OF TASTE
§Taste buds adapt within 1-5 minutes of continuous stimulation
§Some occurs at taste receptors §Mostly occurs in CNS
§Bitter taste buds are minimally adapted
SENSE OF TASTE AND CONTROL OF DIET
§Taste preference
§Selection of certain types of foods in preference to others §Changes with needs of the body for specific substances
§Past experience with the food §Occurs at CNS
Taste aversion
§Avoidance of food that has caused illness in the past ‘negative taste preference’ §Occurs at CNS
§Advantage is longer survival
APPLIED GUSTATORY PHYSIOLOGY
Ageusia
§Hypogeusia
§Diminished taste sensitivity §Old age and various diseases §
Dysgeusia
§Disturbed sense of taste §Lesions in gustatory cortex
Ageusia
deficiency of Vit B3 & Zinc oCushing’s syndrome
oDiabetes
oHypothyroidism
oSide Effects of
oAntirheumatic drugs
oPenicillamine oAntiproliferative drugs oCisplatin
oACE inhibitors
oAzelastine
oClarithromycin
oZopiclone
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself