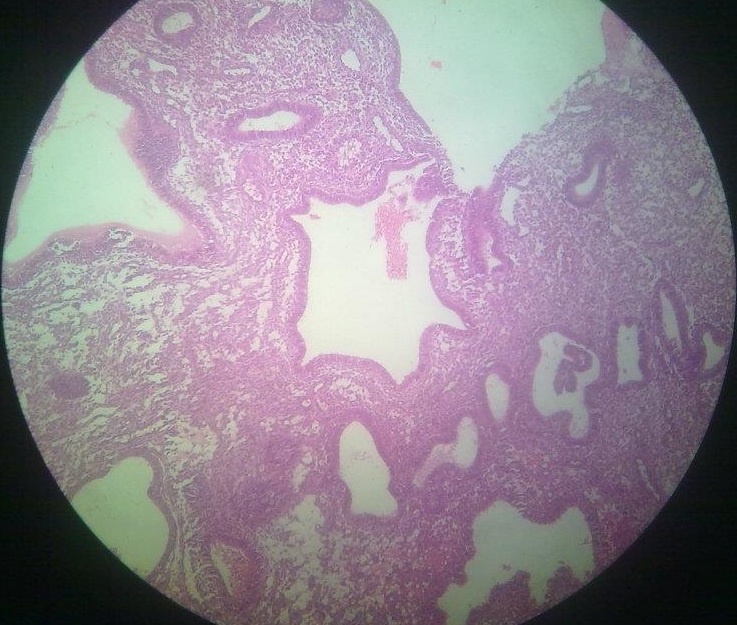
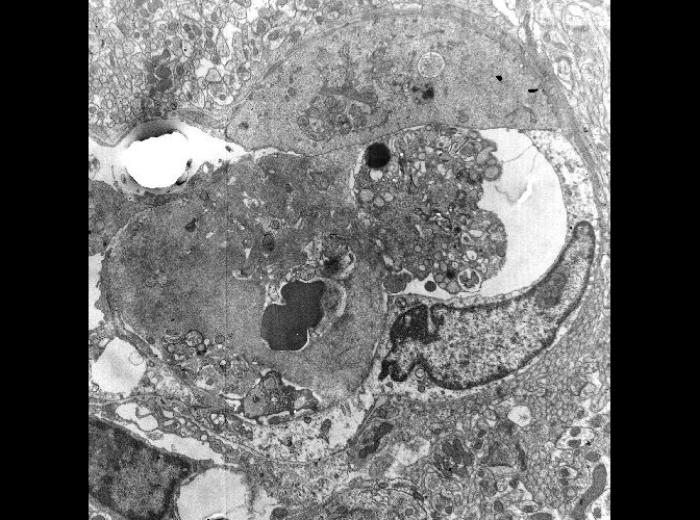
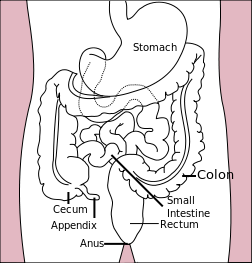
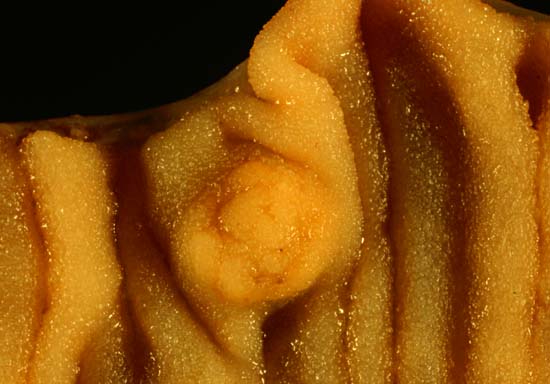
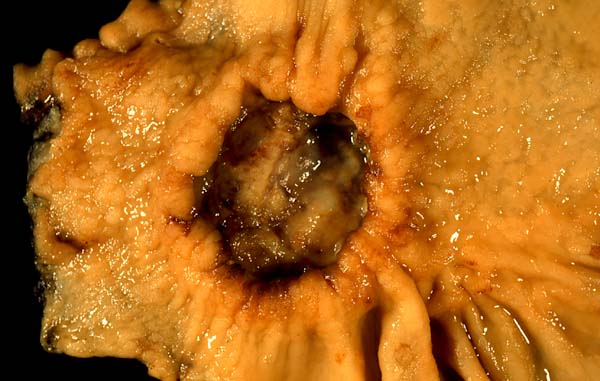
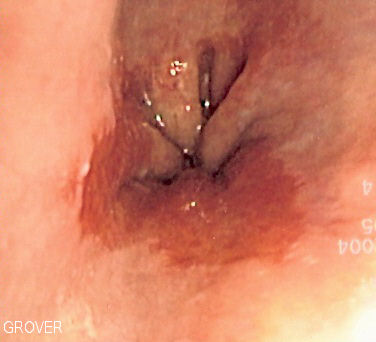
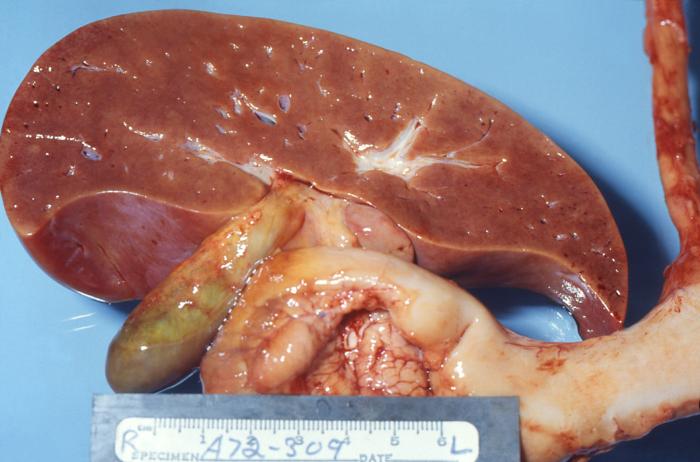
It is the most common example. The proliferative activity of endometrium is controlled by increased estrogen, which is then stopped … Read More »
Hypertrophy
Hypertrophy is the increased size of cell, due to increased synthesis of structural components. It may be because of increased … Read More »
Classification of Tumors of Colon and Rectum
Tumors of colon and rectum may be classified, based on histology, into: 1. Epithelial tumors: a. Adenoma: i. Tubular ii. … Read More »
Classification of Tumors of Small Intestine
Tumors of small intestine may be classified, based on histology, into: 1. Epithelial tumors: a. Adenoma i. Tubular ii. Villous … Read More »
Classification of Tumors of Stomach
Tumors of stomach may be classified, based on histology, into: 1. Epithelial tumors: a. Intraepithelial neoplasia -Adenoma b. Carcinoma: i. … Read More »
Classification of Tumors of Esophagus
Tumors of esophagus may be classified, based on histological features, into: 1. Epithelial tumors: a. Squamous cell papilloma b. Intraepithelial … Read More »
Cell Response to Reversible Injury
In response to injury, cells respond by: Homeostasis: Ability of normal cell to maintain steady state. Adaptations: Adaptations are reversible, … Read More »
Causes of Cell Injury
Life meets change & variation everyday. We make appropriate adjustments, so does the cell “the unit of life”. “Homeostasis” is … Read More »
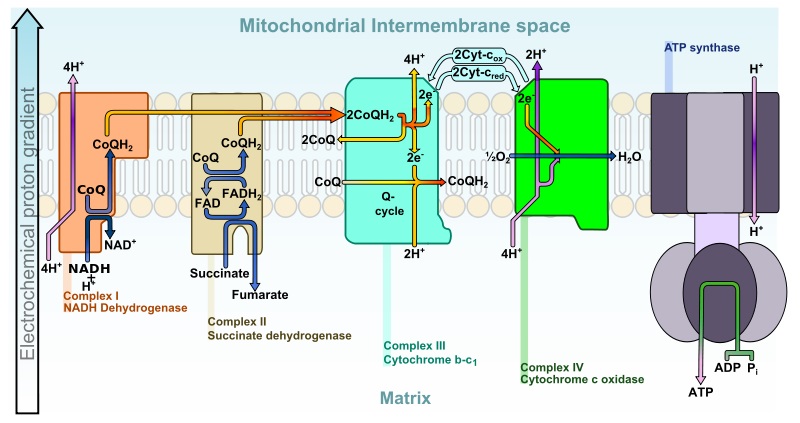
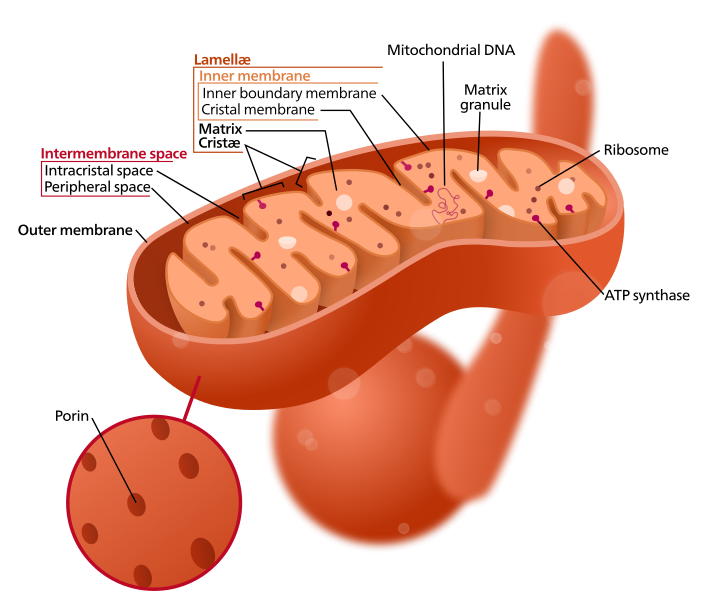
ATP Depletion and Mitochondrial Damage
ATP is generated in the body by Oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria Anaerobic glycolytic pathway (liver) ATP depletion by 5% … Read More »
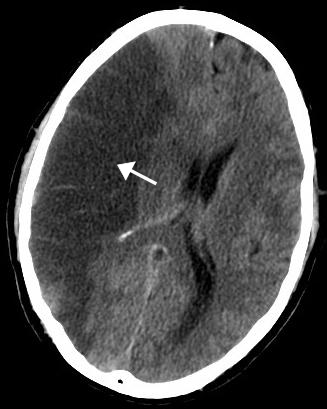
Pathology of Cerebral Ischemia
Cerebral ischemia, also called brain ischemia, occurs when the blood supply to the brain is unable to meet the required … Read More »
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself