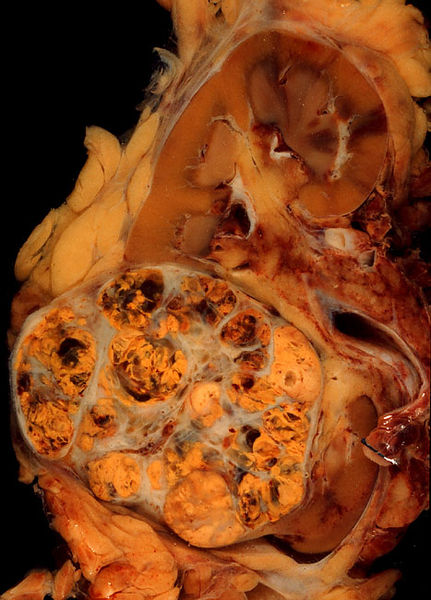
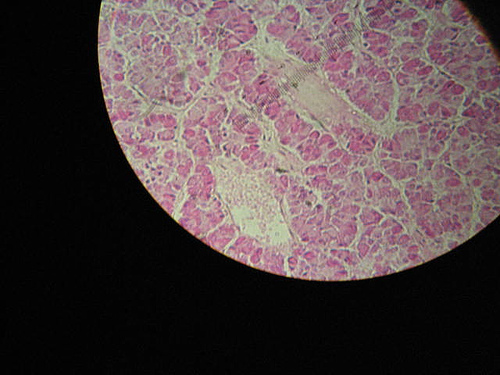
Medication: Ivermectin (Stromectol, Soolantra, Sklice) Price for 12 mg: from …
Read More »-
Ivermectin for Sale, Buy Ivermectin for Humans Online - Secure, Safe Prescription Online
-
Piperazine Citrate and Diethylcarbamazine -Antihelminthic Drugs
-
Vinca Alkaloids, Taxanes, Epipodophyllotoxins, Camptothecins, Hormones, Anti-hormones, Asparaginase, Monoclonal Antibodies and Cytokines
-
Methotrexate, 5-Fluorouracil, Purine Antagonists and Antibiotics Used in Cancer Chemotherapy
-
Alkylating Agents
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is diagnosed from a liver biopsy …
Read More » -
Amyloidosis
-
Intracellular Accumulations
-
Cellular Aging
-
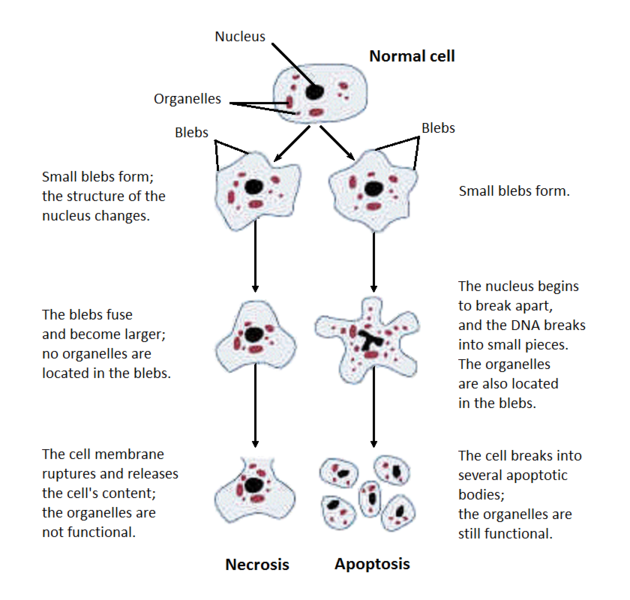
Types of Necrosis
-
Terms Used in Connection with Fertility
Fertility refers to the number of live births women have. …
Read More » -
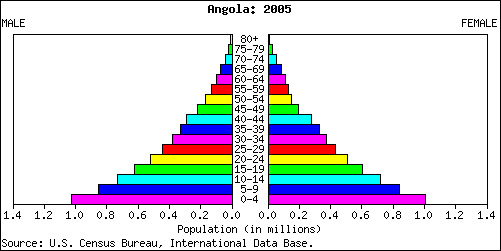
Age and Sex Composition -the Population Pyramid
-
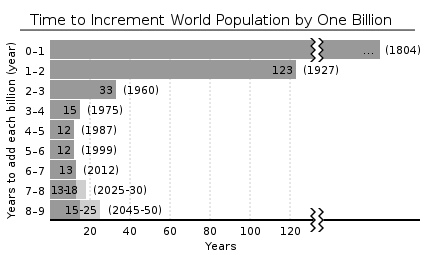
Demography -Introduction and Tools
-
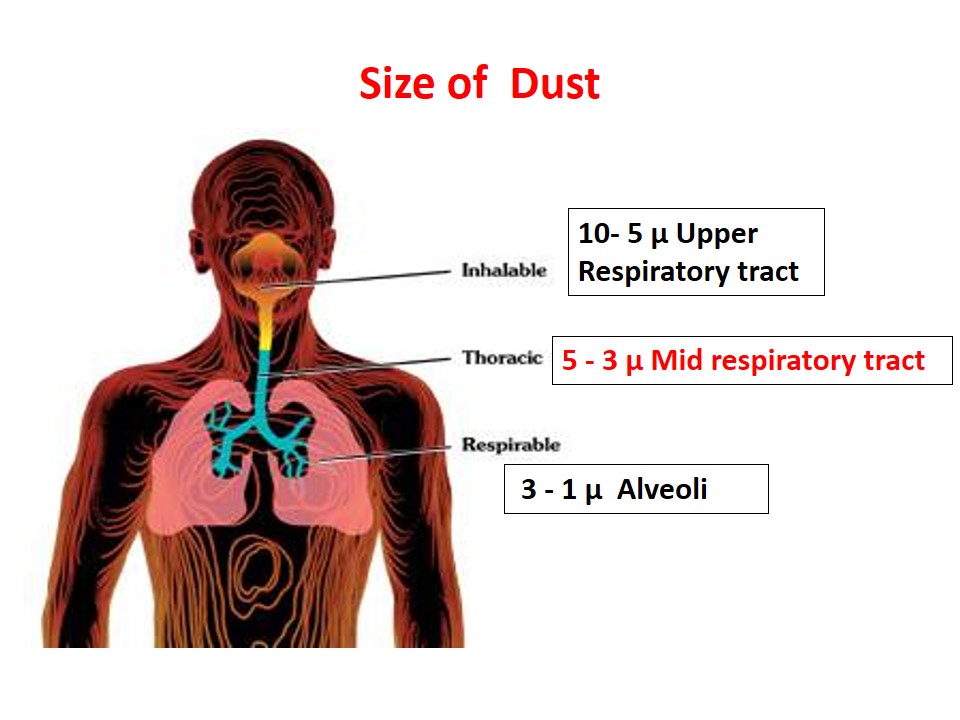
Pneumoconiosis -Types, Silicosis, Asbestosis and Preventive Measures
-
Occupational Health Hazards -Introduction and Types
-
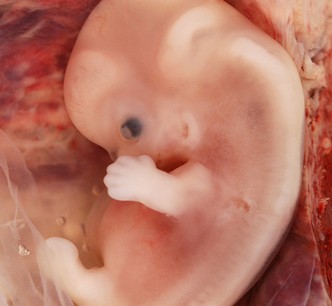
Human Fetal Period
The period from the beginning of the ninth week to …
Read More » -
Birth Defects
-
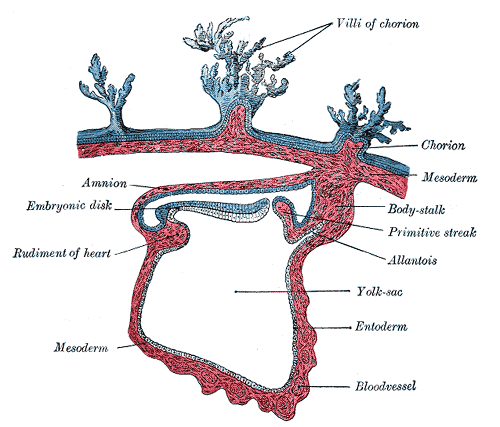
Derivatives of Endoderm (Embryonic Period)
-
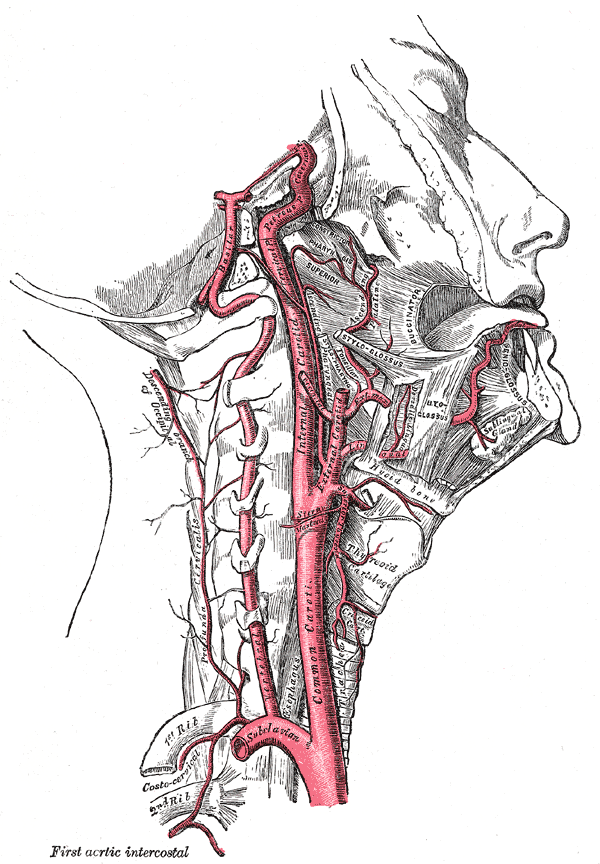
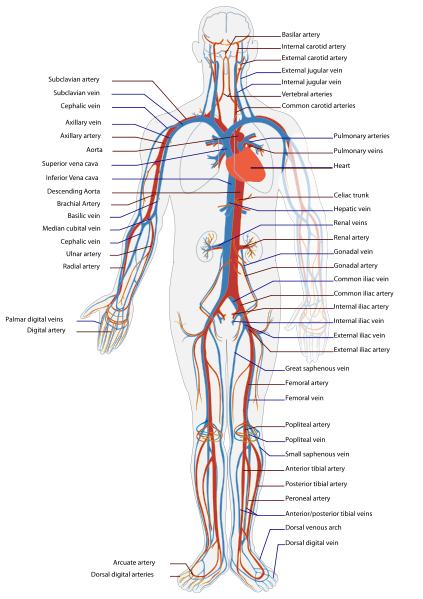
Internal Carotid Artery
-
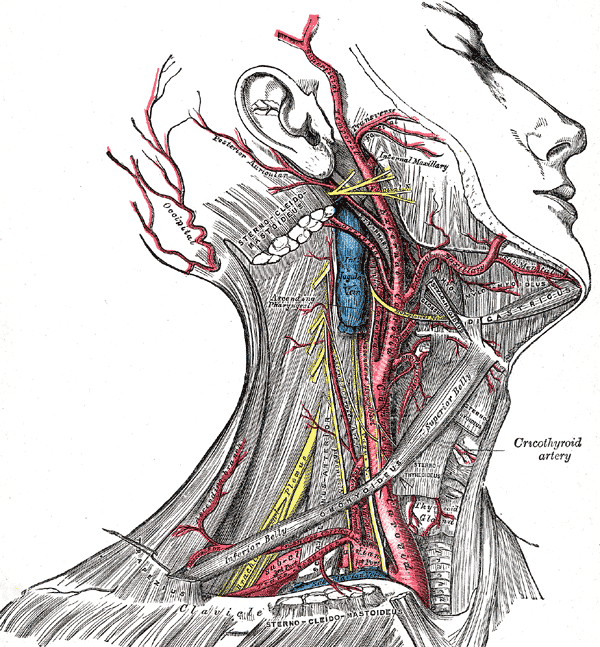
External Carotid Artery
-
Diagnostic Tests of Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes Mellitus is categorized by disorders of carbohydrate, protein and …
Read More » -
Diabetes Mellitus
-
Endocrine Functions of Pancreas
-
Thyroid hormones
-
Case Based Learning: Nutrition
-
Best Ways to Get Fitter and Slimmer
Being fitter and slimmer is not a tricky job now-a-days, …
Read More » -
Nutrition
-
Acid and Base Disorders
-
Easy ways to Loose weight!!
-
Easy and interesting ways to look young
-
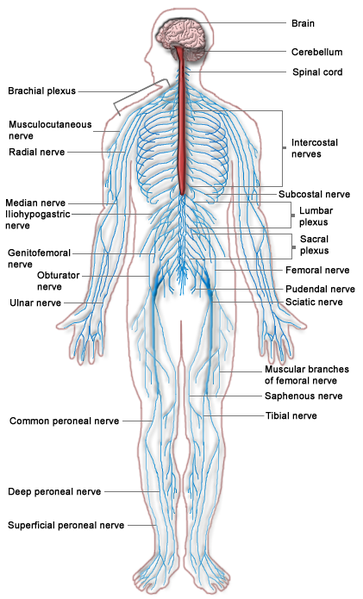
Neurological Examination
Neurological examination should include the following: Examination of Cranial Nerves: …
Read More » -
Neurology History Taking
-
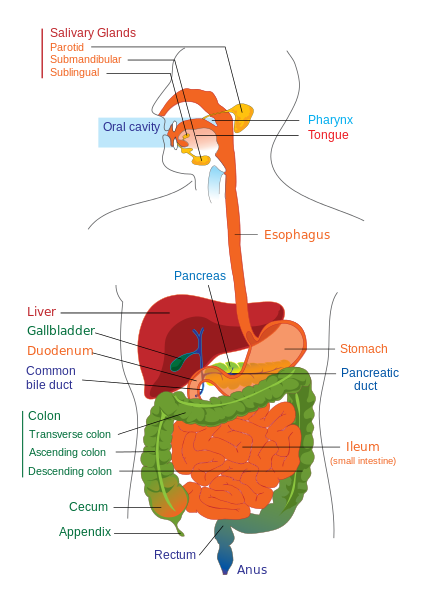
Gastrointestinal Examination
-
Checklist for Posterior Chest Examination
-
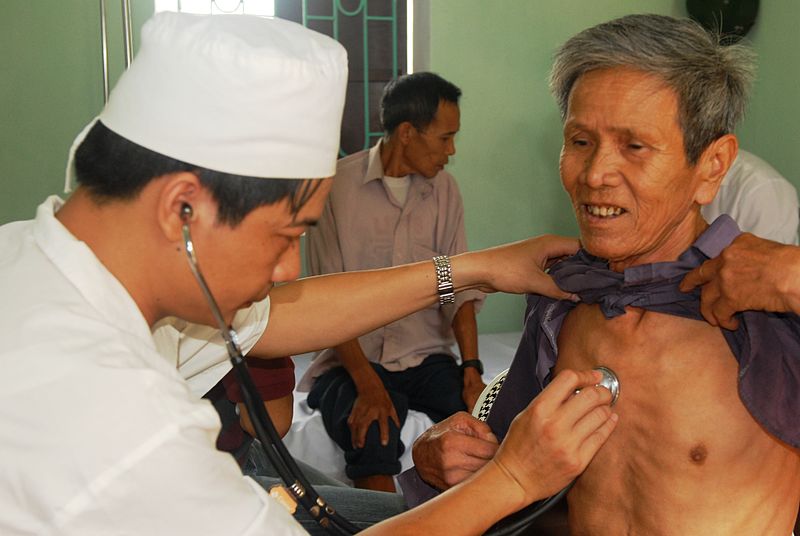
Cardiovascular Examination
-
Hormones of Non Endocrine Glands
Several non endocrine organs and cells also produce hormones, which …
Read More » -
Hypoparathyroidism and Hyperparathyroidism- Disorders of Parathyroid
-
Parathyroid Hormones
-
Hormones- Mechanism of Action, Regulation and Clearance
-
Hormones of Pituitary Gland
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself