Cutaneous mycoses are the diseases caused by fungi and involving the skin, hair and nails. They are different from superficial mycoses as evoke cellular immune response.
Classifications:
Based on Anatomic Location
1. Tinea pedis
2. Tinea capitis
3. Tinea corporis
4. Tinea cruris
Based on Ecologic location
1. Geophilic
2. Zoophilic
3. Anthrophilic
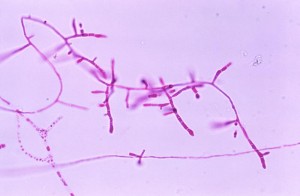
Dermatophytosis
Dermatophytosis are caused by fungi belonging to following genera:
- Trichophyton
- Epidermophyton
- Microsporum
They infect only superficial keratinized tissue(skin, nails, hair) and are classified as geophilic, zoophilic or anthropophilic. They are acquired by contact with contaminated soil, animals or humans.
| Clinical Name | Site | Most frequent organisms |
| Tinea capitis (epidemic) | scalp | Trichophyton tonsuruns, Microsporum audouinii |
| Tinea capitis (non-epidemic) | scalp | Microsporidium canis, Trichophyton verrucosum |
| Tinea pedis | interdigital space | T. rubrum, T. mentagrophytes, Epidermophyton floccosum |
| Tinea barbae | beard | Trichophyton rubrum, T. verrucosum |
| Tinea corporis | arms, legs,torso | T. rubrum, M. canis, T. mentagrophytes |
| Tinea cruris | groin | T. rubrum, T. mentagrophytes, Epidermophyton floccosum |
| Tinea manus | hands | T. rubrum, T. mentagrophytes |
| Tinea unguium | nails | T. rubrum, T. mentagrophytes, E. floccosum |

Clinical Findings
- Raised circular lesions
- Tinea pedis is the chronic infection of toe webs, other varieties are vesicular, ulcerative and of moccasin type with hyperkeratosis
- Tinea unguium with yellow, brittle, thickened and crumbled nails
- Tinea corporis containing annular lesions with a clearing, scaly center surrounded by red advancing border, vesicle formation and pruritis
Diagnosis
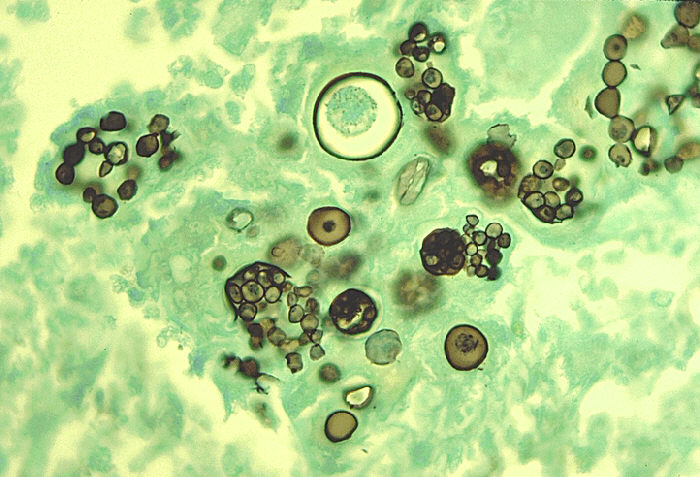
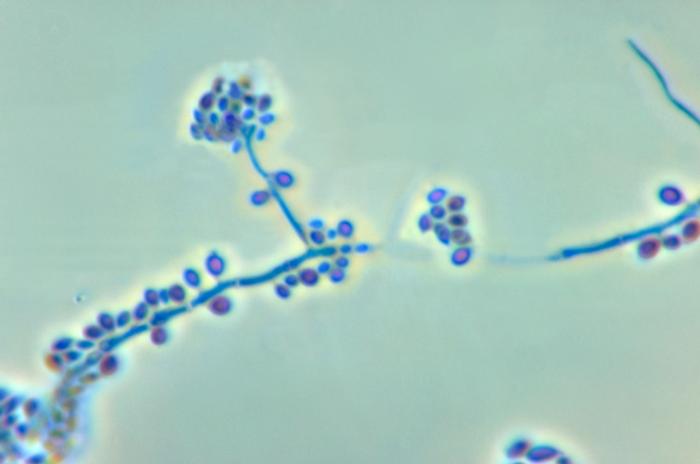
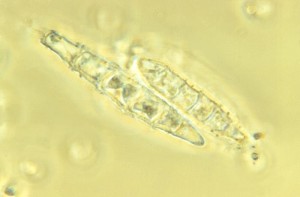
1. Scrapings from skin, nails and hair
2. Microscopic examination of specimen on slide in a drop of 10-20% KOH
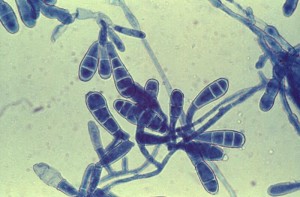
3. Branching hyphae or chains of arthroconidia
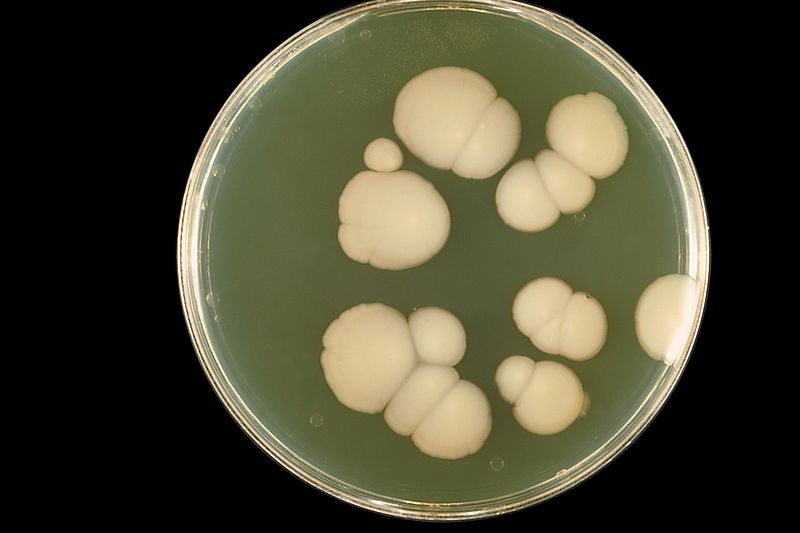
4. Culture on Sabouraud’s dextrose agar and Sabouraud’s dextrose agar with chloramphenicol. Dermatophyte test medium (DTM) may be used as well.
Identification on basis of colonial morphology, growth rate, surface texture, microscopic morphology and nutritional requirements.
Treatment:
Treatment consists of topical antifungal agents.
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself